😏 Core Java Classes Brief Introduction Topics :
#Abstract Class :An Abstract Class is a class that is declared keyword abstract. it may or may not include an abstract method
Abstract method:
A method that is a declared as abstract and does not have an implementation.
abstract class GraphicObject {
int x, y;
...
void moveTo(int newX, int newY) {
...
}
abstract void draw();
abstract void resize();
}
#Interface class :
An interface class in java is a blueprint of a class, it has static constant and abstract method.there can be the only abstract method in Java interface .(is-a relationship)
The Interface class can look something like this:
interface Bicycle { // wheel revolutions per minute void changeCadence(int newValue); void changeGear(int newValue); void speedUp(int increment); void applyBrakes(int decrement); }
#Marker Interface :
it is an empty interface (on field or method )
The Interface class can look something like this:
interface Bicycle { //empty}
Cloneable Interface :
The Cloneable interface is present in java.lang.package. there is a method clone() in the object class
A class that implements the Cloneable interface indicates that itis legal for clone() method to make a field for field copy of an instance of that class.
Serializable Interface :
The Cloneable interface is present in java.lang.package. there is a method clone() in the object class
A class that implements the Cloneable interface indicates that itis legal for clone() method to make a field for field copy of an instance of that class.
Serializable Interface :
The Serializable interface is present in the java.io package. It is used to make an object eligible for saving its state into a file. This is called Serialization.
Classes that do not implement this interface will not have any of their state serialized or deserialized. All subtypes of a serializable class are themselves serializable.
Remote interface :
The remote interface is present in java.rmi package. A remote object is an object which is stored at one machine and accessed from another machine. So, to make an object a remote object, we need to flag it with the Remote interface.
Here, Remote interface serves to identify interfaces whose methods may be invoked from a non-local virtual machine.Any object that is a remote object must directly or indirectly implement this interface.
RMI (Remote Method Invocation) provides some convenience classes that remote object implementations can extend which facilitate remote object creation.
Remote interface :
The remote interface is present in java.rmi package. A remote object is an object which is stored at one machine and accessed from another machine. So, to make an object a remote object, we need to flag it with the Remote interface.
Here, Remote interface serves to identify interfaces whose methods may be invoked from a non-local virtual machine.Any object that is a remote object must directly or indirectly implement this interface.
RMI (Remote Method Invocation) provides some convenience classes that remote object implementations can extend which facilitate remote object creation.
#Wrapper Class :
A wrapper class is a class where object wraps or contains a primitive type.
when we create an object to wrapper class, it contains a field and infield, we can store a primitive datatype, in other words, we can wrap a primitive value into a wrapper class object.
Need od wrapper class :
- They convert primitive datatype into the object, object are needed if we wish to modify the arguments passed into a method.
- the classes in java.util package handle only object and hance wrapper classes help in the case also
- A data structure in the collection framework, such as ArrayList and vector, store the only object and not the primitive type.
- An object is needed to support synchronized in multithreading
Primitive Datatype and their corresponding wrapper class :


Autoboxing :
Automatic conversion of primitive type to the object of their corresponding wrapper class is known as autoboxing.

Unboxing :
it is just the reverse process of autoboxing. automatically converting an object of wrapper class to it corresponding primitive type is known as unboxing.
#Casting Class :
#Casting Class :
Casting Really means in taking an object of one particular type and "turning it into" another object type. this process is called casting a variable.
Type Casting :
Assigning a value of one type to a variable of another type is known as typecasting.
Type Casting is classification into two type :
Widening casting (Implicit) :


- The target type is larger than the source type.
- it is automatic type conversion.
- JVM will create new object type.
Narrowing casting (Explicitly):
when you are assigning a larger type value to a variable of small type, the need to perform explicitly.
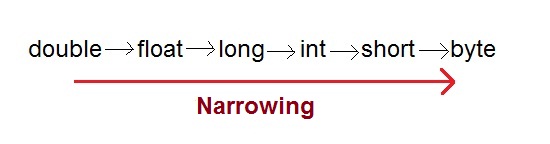
when you are assigning a larger type value to a variable of small type, the need to perform explicitly.

- Larger type value to the variable of small type value.
- the program will create new object typeset.
#Stream Class:
A stream can be defined as a sequence of data. hierarchy of classes for input and output streams.
the input stream is used to read data from a source and the output stream is used for writing data to a destination. to perform read and write operation on binary files we need a mechanism to read that binary data on file / to write binary (i.e. in the form of byte)

We can define our own classes with generics type. A generic type is a class or interface that is parameterized over types. We use angle brackets (<>) to specify the type parameter.
class MyGen <T> {
T obj;
void add (T obj){ this.obj=obj; }
T.get(){
return obj;
}
}
Generic method :
Like a generic class, we can create the generic method that can accept any type of argument.
public static<E> void printArray(E[] elements){
for(E element:elements){
System.out.println(element);
}
}
Thanks for sharing this good blog.This is very important and imformative blog for Java . very interesting and useful for students
ReplyDeleteCore Java Online Training
Thanks for sharing wonderful Information
ReplyDeleteRPA TRAINING IN PUNE
nice post.
ReplyDeleteazure training
java training
salesforce training
hadoop training
mulesoft training
linux training
mulesoft training
web methods training